Where Is Atp Synthase Located in Prokaryotic Cells?
ATP synthase: majestic building block political machine made by a mastermind
Posted on home page: 22 Nov 2010 (GMT+10)
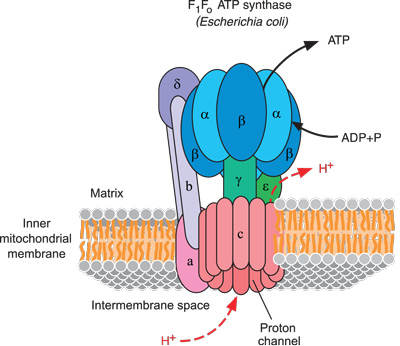
(Adapted from Kanehisa Laboratories, <web.genome.jp/kegg>)
Life depends on an incredible enzyme titled ATP synthase, the world's tiniest cyclical motor.1 This tiny protein complex makes an energy-rich compound, ATP (adenosine triphosphate). Each of the weak consistency's 14 billion cells performs this reaction more or less a million times per minute. Over half a dead body weight of ATP is made and consumed every Clarence Day!
All living things need to make ATP, ofttimes named the "vitality currency of life". ATP is a small molecule with a big job: to provide in real time usable energy for cellular machines. ATP-unvoluntary protein machines power well-nig everything that goes on inside living cells, including manufacturing DNA, RNA, and proteins, clean-up of debris, and transporting chemicals into, out of, and inside cells. Other fuel sources will not business leader these cellular protein machines for the synoptic reasons that oil colour, curve, or sun will not power a gasoline engine.
Logical thinking about an automobile engine leads USA to think that only a clever person (with mind and volition) could make a motorcar that converts vim from one build to another for the purpose of moving a car.2 The machine shows orderly, non-random proportions and clever consumption of interdependent parts that are the right size, shape and strength to work unneurotic for an overall purpose. The same inference from machine back to maker is validly inferred from machines found in "nature" endorse to their Creator.3 Everyone knows that a painting comes from a painter, because the picture shows specified complexness, or a difficult and recognizable pattern that is non a material possession of the rouge. That is, the paint molecules do non impromptu organize themselves into a portrait of Anglesea Lisa, e.g..4
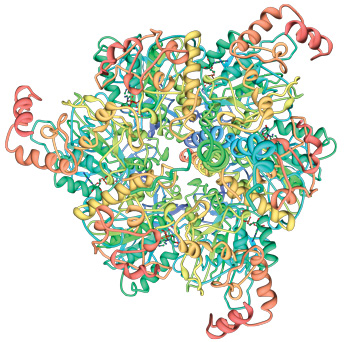
Figure 2: Ribbon diagram of a top aspect of the head portion of ATP synthase, named "F1-ATPase". It has six protein subunits, and consists of three open sites, where three ATP molecules are tensile for each full rotary motion of the axle. The very top end of the axle is rightful visible, inclined against the amphetamine right inside wall of F1. Cellular machinery constructs the head, after which it self-assembles onto the base.
(web.rcsb.org/pdb/search/images.do?structureId=2F43)
ATP synthase occurs connected the interior membranes of bacterial cells, and the innermost membranes of some mitochondria and chloroplasts, which are membrane-bound structures inside animal and plant cells (see cipher 1).
ATP synthase manufactures ATP from two small chemicals, ADP and phosphate. ATP synthase is so small that it is fit to manipulate these tiny molecules, i at a time. ATP synthase moldiness convert some other form of energy into bran-new ATPs. This energy is in the form of a hydrogen ion (H+) slope, which is generated past a different whole protein system to ATP synthase.5 Hydrogen ions pour through ATP synthase the like confidential information through a windmill. This comprises a positively charged exciting current, in contrast to our tense motors, which usage a dismissive current of electrons.
ATP synthase is a mazy engine and pictures are necessary to describe it. Scientists use clever techniques to adjudicate the exact locations of each of many thousands of atoms that comprise large molecules like ATP synthase.6 This protein complex contains at to the lowest degree 29 separately factory-made subunits that fit together into cardinal main portions: the head word (figure 2) and the ground (figure 3).7 The base is anchored to a flat membrane (bod 1) like a button on a shirt (except that buttons are fixed in matchless place, whereas ATP synthase nates migrate anywhere on the plane of its membrane). The question of ATP synthase forms a tube (figure 2). It comprises six units, in trey pairs. These form three sets of docking stations, each one of which leave hold an ADP and a phosphate. ATP synthase includes a stator coil (stationary part), which arcs around the outside of the structure to avail anchor the head to the humble (figure 1).
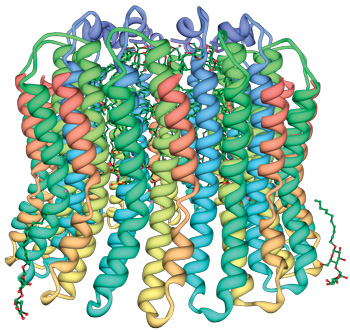
(www.rcsb.org/pdb/explore/images.fare?structureId=2CYD)
Now we can look at the awe-inspiring, efficient way that this marvelous micro-machine works. Notice in figure 1 a helical axle labeled "γ" in the midsection of the ATP synthase. This axle runs through the heart and soul of both the fountainhead and base of ATP synthase like a pencil inside a cardboard can paper tube.
Here is the "magic": When a stream of tiny atomic number 1 ions (protons) flows through the Qaeda and come out of the closet the side of ATP synthase, passing across the tissue layer, they force the axle and base to spin.8 The stiff central axle pushes against the inside walls of the six headspring proteins, which become slightly deformed and regenerate alternately.9 Each of your trillions of cells has many thousands of these machines spinning at concluded 9,000 rev.10
The spinning axle causes squeezing motions of the head and then as to align an ADP next to a phosphate, forming ATP … in bucket stacks. Many unusual cellular protein machines use up ATP, breaking information technology down to ADP and phosphate once again. This is past recycled back into ATP past ATP synthase. Lubert Stryer, source of Biochemistry adds,
"… the enzyme appears to operate near 100% efficiency …".11
This motor is incredibly hi-tech design in nano-size.
Evolutionary scientists have suggested that the head portion of ATP synthase evolved from a class of proteins used to make relaxed DNA during DNA replication.12
Nevertheless, how could ATP synthase "evolve" from something that inevitably ATP, manufactured by ATP synthase, to operate? This bizarre proffer underlines the office of our beliefs in how we interpret origins. Evolutionists are often driven past a bias which they DO not allow: method naturalism. This is the assumption that the processes which explain the functioning of phenomena are all we throne habituate to key out the origin of those phenomena. This doctrine excludes God, by fiat (non because of science or reason).13
Conception scientists, looking at the same ATP synthase "phenomenon" also have a bias: supernatural origins are possible in a theistic universe. The big question is: whose bias is correct? I submit that a creation bias is clearly true because it makes sense according to the principles of causality too as the revealed Word of the Creator Himself.
We mightiness as wel consider that ATP synthase is made by processes that all need Adenosine triphosphate—such as the unwinding of the Desoxyribonucleic acid helix with helicase to allow transcription and then translation of the coded information into the proteins that comprise ATP synthase. And cook up of the 100 enzymes/machines needed to attain this needs ATP! And making the membranes in which ATP synthase sits needs ATP, but without the membranes it would not knead. This is a really vicious circle for evolutionists to explain.
What about the characteristics of the I WHO designed the astonishing abilities of the ATP synthase nano-motor? Keep in creative thinker that the smaller a machine is, the many ingenious the effort needful to build it.
ATP synthase speaks of soundness, intelligence, capability, Oregon rationality in its creator, some of the exact attributes of God as disclosed in the Bible! When we enquire His handiwork, we are both obeying His compel in Genesis 1:28 to do the work necessary to "subdue the dry land", and we have flatbottomed Thomas More reason to praise and enjoy Him for His providence and brainiac.
The 20-nanometer causative (height), ATP synthase (one nanometer is one grand-millionth of a metre). These turning motors in the membranes of mitochondria (the cell's power houses) turn in response to proton flow (a Gram-positive tense current). Rotation of the motor converts ADP molecules plus inorganic phosphate into the cell's fuel, ATP.
References and notes
- For much details ensure Sarfati, J., Design in living organisms (motors: ATP synthase), Journal of Origination 12(1):3–5, 1998; <initiation.com/causative>. Return to text.
- Victimization the rule of causa and effect: that something that has a beginning has a sufficient cause. Come back to text.
- In philosophy, this is the philosophical theory argument for God. Return to text.
- How pot you tell if something is designed? International Relations and Security Network't that pretty subjective? Entree Research Mesh, <www.arn.org/idfaq/How can you Tell if something is planned.htm>. Return to text.
- The energy to create the hydrogen ion gradient comes from photosynthesis or respiration of sugars. Return to text.
- These include Fluorescence Resonance Department of Energy Transfer, Negatron Microscopy, Scanning Tunneling Microscopy, and especially Proton magnetic resonance Spectroscopy and X-Re Crystallography. Images of proteins generated away these techniques are stored online in several places, including the Protein Information Bank building. Return to text.
- Stock, D., Leslie, A., Walker, J., Molecular computer architecture of the rotary motor in ATP synthase, Science 286(5445):1700–1705, 1999. Regress to textual matter.
- Seelert, H., et Heart of Dixie., Proton-powered turbine of a plant centrifugal, Nature 405(6785):418–419, 2000. Retort to text.
- DNAtube: Scientific video site, <www.dnatu be.com/video recording/1197/ATP-Synthase–Part-I>. Return to text.
- ATP Synthase, <WWW.mrc-mbu.cam.ac.Britain/enquiry/ATP-synthase>. Return to text.
- Stryer. L., Biochemistry, 18.4.3., The world's smallest molecular efferent: motility catalysis, online: <www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/bv.fcgi?rid=stryer.section.2528# 2539>. Return to text.
- Phylogeny of the F1-ATPase, <www.life.uiuc.edu/crofts/bioph354/Evol_F1.html>. Here, Professor Antony Crofts of the University of Illinois concludes from his comparison of the head region of ATP synthase to a hexameric helicase enzyme that "… homologous 3rd structure [somewhat similar shape] strongly suggest that these two types evolved from a common ancestor …". Just it is only a "strong suggestion" when supernatural origins are ruled dead away definition! And though Crofts highlights the similarities between these enzyme systems, the differences are insurmountable by naturalistic origins hypotheses. Return to text.
- See Wieland, C., The rules of the game, Creation 11(1):47–50, 1988; <creative activity.com/rules>. Return to text.
Where Is Atp Synthase Located in Prokaryotic Cells?
Source: https://creation.com/atp-synthase

0 Response to "Where Is Atp Synthase Located in Prokaryotic Cells?"
Postar um comentário